Known by many names, including Hardy Terrestrial Orchids, Moccasin Flower, and Squirrel Foot, the Lady Slipper Orchid is a fascinating perennial from the Cypripedium genus in the Orchidaceae family. Native to regions across the Northern Hemisphere and Central America, this plant thrives in temperate zones and is admired for its unique shapes and striking color patterns.
Lady Slipper Orchids are among the most primitive orchids still found today, with most species growing terrestrially in the ground. While captivating, some varieties are rare or even endangered, making them a prized yet delicate addition to any garden.
| Common name | Hardy Terrestrial Orchids, Lady Slipper Orchid, Moccasin Flower, Slipper Orchid, Squirrel Foot |
| Botanical name | Cypripedium |
| Family | Orchidaceae |
| Origin | Northern Hemisphere to Central America |
| Life cycle | Perennial |
| Plant type | Native Plant |
| Hardiness zone | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 |
| Sunlight | Partial Shade |
| Maintenance | Low |
| Soil condition | Loam |
| Soil ph | Acid |
| Drainage | Well-Drained |
| Growth rate | Slow |
| Spacing | Less than 12 in. |
| Flowering period | Spring |
| Flower color | Gold, Yellow |
| Leaf color | Green |
| Fruit type | Capsule |
| Flower benefit | Showy |
| Garden style | Cottage Garden |
| Uses | Container |
I. Appearance and Characteristics
Cypripedium is a genus of 58 species and nothospecies of hardy orchids; it is one of five genera that together compose the subfamily of lady’s slipper orchids (Cypripedioideae). They are widespread across much of the Northern Hemisphere, including most of Europe and Africa (Algeria) (one species), Russia, China, Central Asia, Canada the United States, Mexico, and Central America.
They are most commonly known as slipper orchids, lady’s slipper orchids, or ladyslippers; other common names include moccasin flower, camel’s foot, squirrel foot, steeple cap, Venus’ shoes, and whippoorwill shoe. An abbreviation used in trade journals is “Cyp.” The genus name is derived from Ancient Greek Κύπρις (Kúpris), an early reference in Greek myth to Aphrodite, and πέδιλον (pédilon), meaning “sandal”.
Most Cypripedium grow in temperate and subtropical climates, but some species grow in the tundra in Alaska and Siberia, which is an unusually cold habitat for orchids. Other species occur well into tropical areas such as Honduras and Myanmar.
Some of the northern species can withstand extreme cold, growing under the snow and blooming when the snow melts. But, in the wild, some have become rare and close to extinction, due to an ever shrinking natural habitat and over-collection, people prizing the flowers for their beauty. Several species are legally protected in some regions. In the late 20th century, only a single known plant of Cypripedium calceolus survived in Britain.
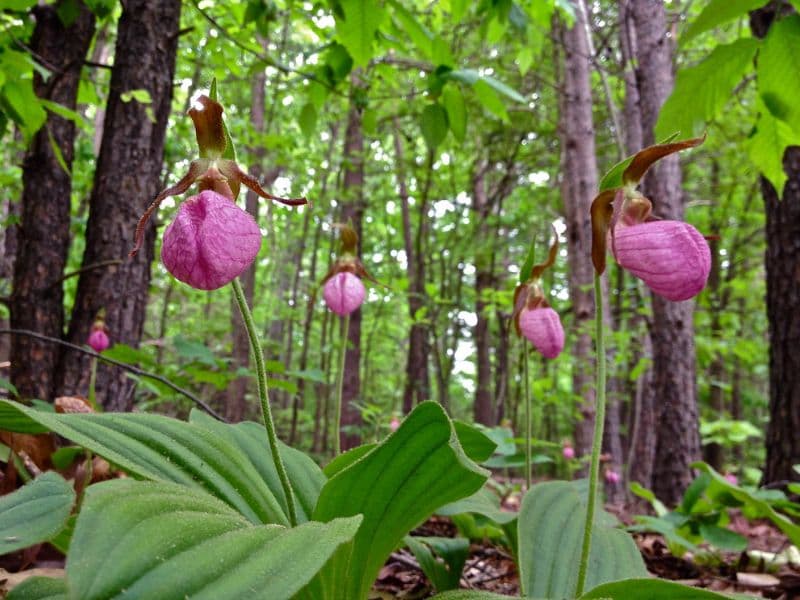

The Cypripedium are terrestrial and, as with most terrestrial orchids, the rhizome is short and robust, growing in the uppermost soil layer. The rhizome grows annually with a growth bud at one end and dies off at the other end. The stem grows from the bud at the tip of the rhizome.
Most slipper orchids have an elongate erect stem, with leaves growing along its length. But the mocassin flower or pink lady’s slipper (Cypripedium acaule) has a short underground stem with leaves springing from the soil. The often hairy leaves can vary from ovate to elliptic or lanceolate, folded (plicate) along their length. The stems lack pseudobulbs.
The inflorescence is racemose. It can carry one to twelve flowers, as in Cypripedium californicum. But most species have one to three flowers. There are three sepals, with, in most species, the two lateral ones more or less fused. The flower has three acute petals with the third a striking slipper-shaped lip, which is lowermost. The sepals and the petals are usually similarly colored, with the lip in a different color. But variations on this theme occur.
The aspect of the lip of different species can vary a great deal. As with all orchids, it is specially constructed to attract pollinators, which it traps temporarily. The flowers show a column with a unique shield-like staminode. The ovary is 3-locular (with three chambers).
II. How to Grow and Care
Sunlight
This is a low-light orchid that requires shade. Place it in an east-facing or a shaded south-facing window. Fluorescent lighting also works well. Suspend lights 6 to 12 inches above the foliage. Grown outdoors, some varieties of these terrestrial orchids prefer full sun in the morning with afternoon shade. Other varieties prefer only dappled sun throughout the day.
Temperature
Mottled leaf types thrive in daytime temperatures between 75 and 85 degrees F. and nighttime temperatures from 60 to 65 degrees F. Keep green leaf types between 75 and 80 degrees F. during the day and 50 to 60 degrees F. at night. These are recommended temperatures, but many growers are successful growing both types in the same temperature range.
Moderate humidity of 40 to 50 percent is adequate and can be maintained by setting the orchid pot on a tray of gravel partially filled with water. Water should not touch the bottom of the pot. If humidity is low avoid letting moisture sit on the leaves or crown of the plant. When humidity is high, air movement is essential which might require a fan or dehumidifier.
For the varieties that prefer boggy conditions, humidity levels may need be higher. Those varieties will also require a temperature drop of 10 to 15 degrees overnight.
Watering
Like other sympodial orchids, lady slipper orchid stems have pseudobulbs for storing water and nutrients, so they can go a while between waterings without suffering. Depending on the growing environment, your orchid may need water twice a week.

Avoid chemically treated water or allow it to sit out for several days before using. Potting medium should stay moist but never soggy, though some varieties that grow in boggy conditions may prefer a wetter medium.
Others can grow indoors but need very specific temperatures, with a 10-15 degree temp drop at night.
Soil
Most are terrestrial orchids that grow in very specific types of soil. Good choices for potting material include shredded osmunda bark, medium grade fir bark and crushed dried oak leaves. Avoid packing the mix too tightly.
Fertilizing
Lady slipper orchids are sensitive to fertilizer; they have fleshy, hairy roots that are easily burned if too much fertilizer is applied. How often and what strength to add depends partly on the growing medium. Osmunda bark contains nutrients, so it requires less frequent and potent fertilizer solutions. If your orchid is potted in fir bark, use a high-nitrogen fertilizer such as 30-10-10. Suggestions include 1/4 to 1/2 strength applied once every two weeks.
The orchid should be flushed with clear water once monthly to a remove harmful salts.
Pruning
Pruning lady slipper orchids is seldom needed. It is a good idea, though, to examine the plant annually after blooming and add fresh potting materials. Remove any diseased leaves or brown roots to avoid root rot spreading.
Propagation
Lady slipper orchids reproduce in three ways. Thousands of tiny seeds are dispersed by wind but only germinate in specific types of fungi. They also reproduce and colonize through spread of the rhizome. Germination can take several years, and even division seldom produces a plant mature enough to bloom in the first five years. These are complex methods requiring a greenhouse growing environment best left to orchid specialists.
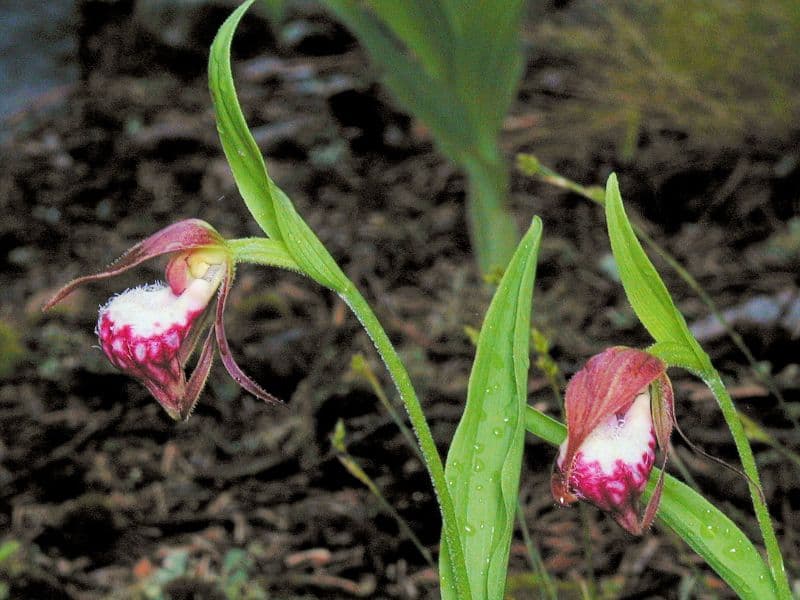

Some varieties form keikis which is the easiest method to propagate your plant. It’s a little more involved then removing a keiki from some other types of orchids, but it can be accomplished with the right patience and care. Gather together a small pot, planting medium, fungicide and a sharp sterile cutting tool, then follow these steps.
- When you see the keiki begin to form, mound up a potting medium around the baby stem, as if to create a pot within the original orchid pot.
- Keep an eye out for the keiki to begin to develop roots.
- Once several viable roots are present, use the blade to remove the baby orchid from the mother plant, making sure to include the roots.
- Treat the cut end of the stem with fungicide. Do not apply fungicide to the roots.
- Place the baby orchid in its own small 2 to 4 inch pot filled with osmunda and/or fir bark and dry shredded leaves.
- Gently but thoroughly water letting all excess drain away. Then place the orchid in shade or in a location that receives very little indirect light.
- Once you see new growth, move the orchid to a more permanent spot, keeping in mind this plant prefers shade and low, dappled light.
Potting and Repotting
Lady slipper orchids fare best when not too pot bound, however they do not need large pots. If you do have a lady slipper orchid that has matured to reproduce new stems, it’s recommended to keep no more than three stems in one pot. Six-inch pots with good drainage holes are sufficient.
The orchid can be repotted every year or two, either in the same pot or a new one. Repotting is done mainly to replace spent material and should take place once the bloom period is complete. This is the best time to examine the orchid and take care of any pruning. Here’s what to do.
- Grasp the main stem and turn the pot upside down. The orchid should slide out easily along with a loose medium.
- Inspect the leaves, roots, and any flower spikes still attached.
- Proceed with necessary pruning. Cut back flower spikes, dried or damaged leaves and spent roots.
- If using the original pot, inspect it for evidence of salt buildup (white chalky areas) or other fungus. Clean and sterilize the pot if necessary or choose a new pot.
- Place the orchid in the pot adding planting medium in and around the roots. Be sure to cover the rhizome. If aerial roots are present, allow them to grow in their natural direction and avoid trying to force them into the pot.
- Water gently but thoroughly and give the orchid several days to a week to recover before continuing regular fertilization.
How to Get to Bloom
Lady slipper orchid blooms can last as long as three months and produce flowers at least once annually. Most produce just one or two flowers but some newer hybrids produce many. After flowering in early summer, lady slipper orchids will die back until the following spring when it begins to grow again.

Support flowering by using a fertilizer slightly higher in phosphorous as the bloom period approaches. Keep the orchid in total darkness at night.
As with all orchids, the best way to insure flowering is to develop a specific, consistent care routine.
Pests and Diseases
Common Pests & Plant Diseases
Mealybugs are the most common pest of lady slipper orchids, identified by small, white, cottony webs on the undersides of leaves. Gently swab affected areas with a q-tip dipped in isopropyl alcohol.
Small dark spots or patches that develop on flowers indicate botrytis petal blight. This is usually the result of too much humidity or poor air circulation. Remove affected parts and try installing a fan or relocate the orchid to a brighter location. Make sure, though, the plant receives only dappled indirect light.
Common Problems
Most issues arise from improper maintenance involving incorrect light exposure, temperature fluctuations, or watering.
Yellowing Leaves With Black Spots
This problem can crop up when the orchid is exposed to cold or wide temperature fluctuations.
Dry or Dark Leaf Tips or Edges
The orchid may be sunburned. Be sure to place it where it receives only dappled, indirect light.
Stunted Growth or Sudden Flower Loss
Always use lukewarm or room temperature water. Cold water can damage roots.
III. Uses and Benefits
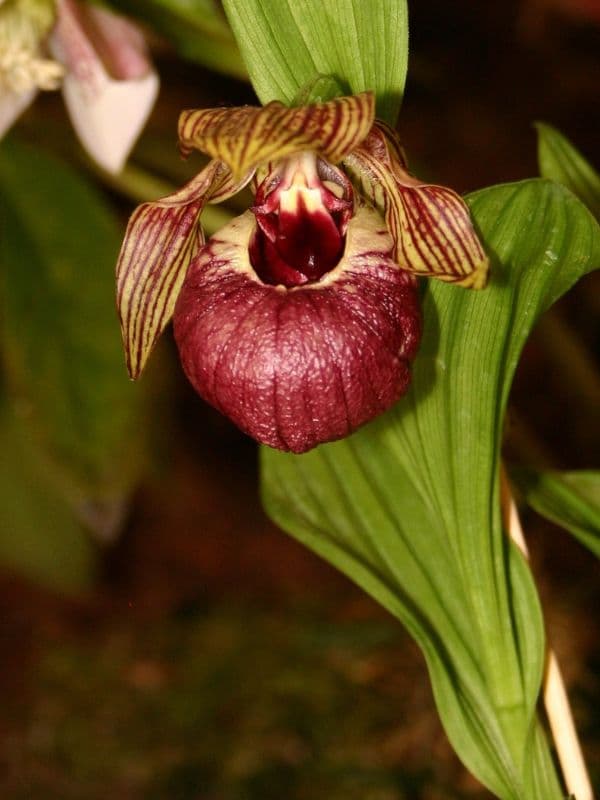

The genus has a long history of use, dating back 2,500 years to the Far East, where they were used medicinally.
IV. Types of Lady Slipper Orchids
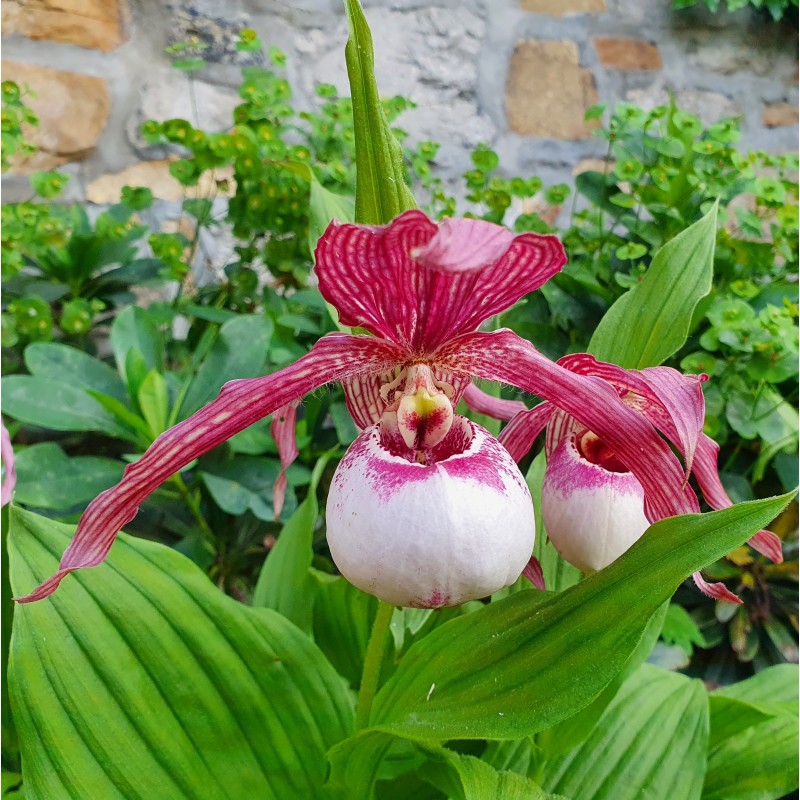
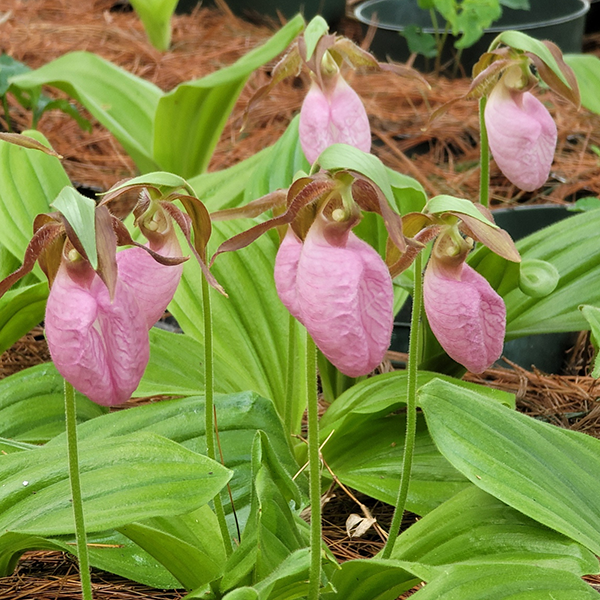
- Cypripedium acaule (pink lady slipper) produces deep pink flowers 3 inches long from late June into July. This is a fragrant type with a sweet floral scent.
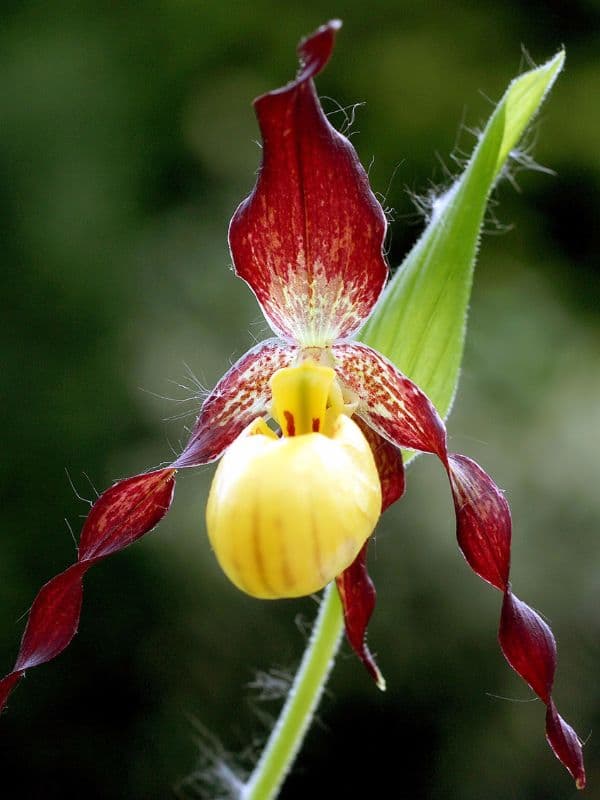
- Cypripedium calceolus (yellow lady slipper) sends up a buttery yellow flower in early spring and is found mostly in rich woodlands or along bog edges.
- Cypripedium parviflorum pubescens (greater yellow lady slipper) can grow up to 2 feet tall, with flower petals up to 6 inches across.
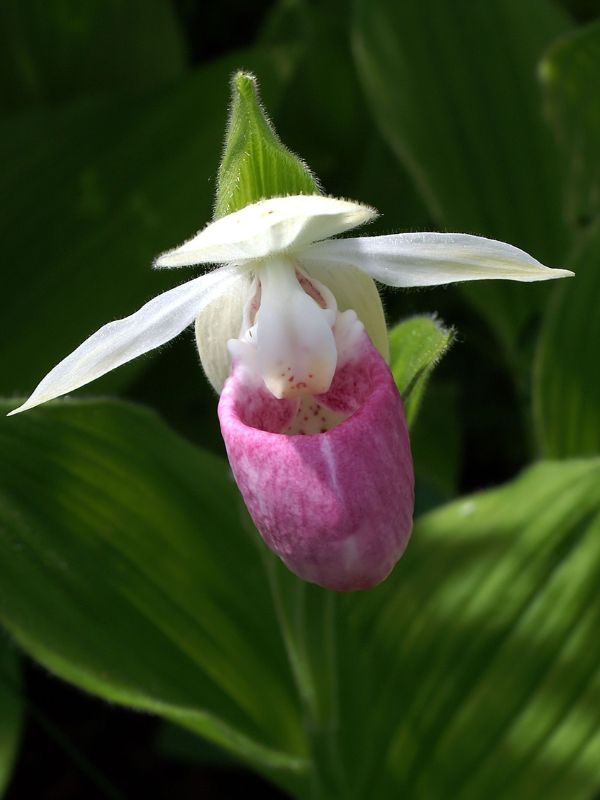
- Cypripedium reginae (showy lady’s slipper) is another large species, 1 to 2 feet tall with pink-streaked, white flowers appearing in late spring/early summer. It grows naturally in wetlands and damp meadows.
- Cypripedium candidum (white lady’s slipper) is a small type from 6 to 12 inches tall. Considered endangered it may be available from reputable nurseries.
Find Where to Buy the Best Lady Slipper Orchid (Cypripedium)















Leave a Reply